Flutter - Introduction
In general, developing a mobile application is a complex and challenging task. There are many frameworks available to develop a mobile application. Android provides a native framework based on Java language and iOS provides a native framework based on Objective-C / Swift language.
However, to develop an application supporting both the OSs, we need to code in two different languages using two different frameworks. To help overcome this complexity, there exists mobile frameworks supporting both OS. These frameworks range from simple HTML based hybrid mobile application framework (which uses HTML for User Interface and JavaScript for application logic) to complex language specific framework (which do the heavy lifting of converting code to native code). Irrespective of their simplicity or complexity, these frameworks always have many disadvantages, one of the main drawback being their slow performance.
In this scenario, Flutter – a simple and high performance framework based on Dart language, provides high performance by rendering the UI directly in the operating system’s canvas rather than through native framework.
Flutter also offers many ready to use widgets (UI) to create a modern application. These widgets are optimized for mobile environment and designing the application using widgets is as simple as designing HTML.
To be specific, Flutter application is itself a widget. Flutter widgets also supports animations and gestures. The application logic is based on reactive programming. Widget may optionally have a state. By changing the state of the widget, Flutter will automatically (reactive programming) compare the widget’s state (old and new) and render the widget with only the necessary changes instead of re-rendering the whole widget.
We shall discuss the complete architecture in the coming chapters.
Features of Flutter
Flutter framework offers the following features to developers −
Modern and reactive framework.
Uses Dart programming language and it is very easy to learn.
Fast development.
Beautiful and fluid user interfaces.
Huge widget catalog.
Runs same UI for multiple platforms.
High performance application.
Advantages of Flutter
Flutter comes with beautiful and customizable widgets for high performance and outstanding mobile application. It fulfills all the custom needs and requirements. Besides these, Flutter offers many more advantages as mentioned below −
Dart has a large repository of software packages which lets you to extend the capabilities of your application.
Developers need to write just a single code base for both applications (both Android and iOS platforms). Flutter may to be extended to other platform as well in the future.
Flutter needs lesser testing. Because of its single code base, it is sufficient if we write automated tests once for both the platforms.
Flutter’s simplicity makes it a good candidate for fast development. Its customization capability and extendibility makes it even more powerful.
With Flutter, developers has full control over the widgets and its layout.
Flutter offers great developer tools, with amazing hot reload.
Disadvantages of Flutter
Despite its many advantages, flutter has the following drawbacks in it −
Since it is coded in Dart language, a developer needs to learn new language (though it is easy to learn).
Modern framework tries to separate logic and UI as much as possible but, in Flutter, user interface and logic is intermixed. We can overcome this using smart coding and using high level module to separate user interface and logic.
Flutter is yet another framework to create mobile application. Developers are having a hard time in choosing the right development tools in hugely populated segment.
Widgets
The core concept of the Flutter framework is In Flutter, Everything is a widget. Widgets are basically user interface components used to create the user interface of the application.
In Flutter, the application is itself a widget. The application is the top- level widget and its UI is build using one or more children (widgets), which again build using its children widgets. This composability feature helps us to create a user interface of any complexity.
For example, the widget hierarchy of the hello world application (created in previous chapter) is as specified in the following diagram −
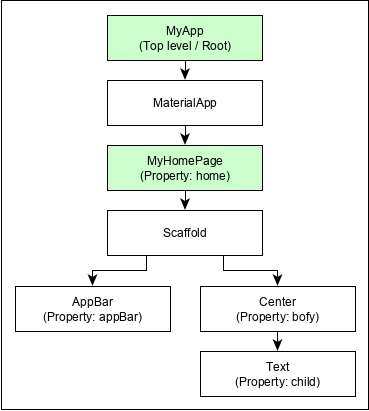
Here the following points are worth notable −
MyApp is the user created widget and it is build using the Flutter native widget, MaterialApp.
MaterialApp has a home property to specify the user interface of the home page, which is again a user created widget, MyHomePage.
MyHomePage is build using another flutter native widget, Scaffold
Scaffold has two properties – body and appBar
body is used to specify its main user interface and appBar is used to specify its header user interface
Header UI is build using flutter native widget, AppBar and Body UI is build using Center widget.
The Center widget has a property, Child, which refers the actual content and it is build using Text widget
Gestures
Flutter widgets support interaction through a special widget, GestureDetector. GestureDetector is an invisible widget having the ability to capture user interactions such as tapping, dragging, etc., of its child widget. Many native widgets of Flutter support interaction through the use of GestureDetector. We can also incorporate interactive feature into the existing widget by composing it with the GestureDetector widget. We will learn the gestures separately in the upcoming chapters.
Concept of State
Flutter widgets support State maintenance by providing a special widget, StatefulWidget. Widget needs to be derived from StatefulWidget widget to support state maintenance and all other widget should be derived from StatefulWidget. Flutter widgets are reactive in native. This is similar to reactjs and StatefulWidget will be auto re- rendered whenever its internal state is changed. The re-rendering is optimized by finding the difference between old and new widget UI and rendering only the necessary changes
Layers
The most important concept of Flutter framework is that the framework is grouped into multiple category in terms of complexity and clearly arranged in layers of decreasing complexity. A layer is build using its immediate next level layer. The top most layer is widget specific to Android and iOS. The next layer has all flutter native widgets. The next layer is Rendering layer, which is low level renderer component and renders everything in the flutter app. Layers goes down to core platform specific code

Leave a Reply